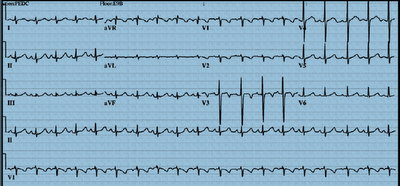
A 16-year-old girl was admitted to the CCU after an aborted
sudden cardiac death. The patient was awakened to answer a telephone call and
suddenly collapsed. The fall was witnessed by people and a rapid 911 call allowed the paramedics
to arrive within couple of minutes. The patient was in VF and was successfully
defibrillated with single shock. She remained comatose and was immediately intubated and
transported to the local hospital.
On physical examination she was intubated and withdrew to painful stimuli. Her
pupils were dilated, but they were reactive to light symmetrically. Her past medical history
is remarkable for 3 brief fainting episodes. She was not using any medication. The mother denied knowledge of substance abuse. Her family history is notable for a sister who died suddenly at the age of 20 years.
What can be the most probablediagnosis at this time?
a. Brugada syndrome
b. HCM
c. RVOT tachycardia
d. Idiopathic VF
e. Long QT syndrome
Please give your answers andcomments in the comment section below.